转载声明:文章来源https://blog.csdn.net/qq_35402412/article/details/79721288
二叉树的概念:
一棵二叉树是结点的一个有限集合,该集合或者为空,或者是由一个根节点加上两棵分别称为左子树和右子树的二叉树组成
二叉树的特点:
1.每个结点最多有两棵子树,即二叉树不存在度大于2的结点
2.二叉树的子树有左右之分,其子树的次序不能颠倒
满二叉树:在一棵二叉树中,如果所有分支结点都存在左子树和右子树,并且所有叶子节点都在同一层上
完全二叉树:如果一棵具有N个结点的二叉树的结构与满二叉树的前N个
结点的结构相同,称为完全二叉树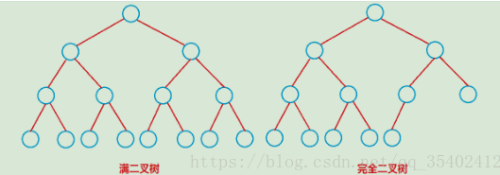
二叉树的基本操作:
0.创建二叉树,前中后序遍历(递归)
1.求二叉树的高度
2.求二叉树叶子结点的个数
3.求二叉树结点的个数
4.求二叉树第K层结点的个数
5.判断一个节点是否在一棵二叉树中
6.获取一个节点的双亲结点
7.获取一个节点的左孩子结点
8.获取一个节点的右孩子结点
9.层序遍历
10.判断一棵二叉树是否为完全二叉树(层序遍历变形)
import java.util.Queue;
import java.util.LinkedList;
import java.util.Iterator;
//节点类
class Node{
private Node left;
private Node right;
private int data;
public Node(int data){
this.data = data;
}
public void setLChild(Node left){
this.left = left;
}
public void setRChild(Node right){
this.right = right;
}
public void setData(int data){
this.data = data;
}
public int getData(){
return this.data;
}
public Node getLChild(){
return this.left;
}
public Node getRChild(){
return this.right;
}
}//二叉树树类
public class Tree{
public Node root; //有一个根节点
public static int index;
public Node CreateBTree( int[] a){
Node root = null;
if(a[index]!='#'){
root = new Node(a[index]);
index++;
root.setLChild(CreateBTree(a));
index++;
root.setRChild(CreateBTree(a));
}
return root;
}
//先序遍历
public void prevOrder(Node root){
if(root==null){
return;
}
System.out.print(root.getData()+",");
prevOrder(root.getLChild());
prevOrder(root.getRChild());
}
//中序遍历
public void inOrder(Node root){
if(root==null){
return;
}
inOrder(root.getLChild());
System.out.print(root.getData()+",");
inOrder(root.getRChild());
}
//后序遍历
public void postOrder(Node root){
if(root==null){
return;
}
postOrder(root.getLChild());
postOrder(root.getRChild());
System.out.print(root.getData()+",");
}
//获取高度
public int getHeight(Node root){
//递归获取
int leftHeight = 0;
int rightHeight = 0;
if(root==null){
return 0;
}else{
leftHeight = getHeight(root.getLeft());
rightHeight = getHeight(root.getRight());
}
return leftHeight >= rightHeight ? ++leftHeight:++rightHeight;
}
//获得叶子数
public int getLeaf(Node root){
if(root==null){
return 0;
}
else if(root.getLChild()==null&&root.getLChild()==null){
System.out.println("Leaf:"+root.getData());
return 1;
}
return getLeaf(root.getLChild())+getLeaf(root.getRChild());
}
//获得第K层节点数
public int getNodeKNum(Node root,int k){
if(k==1){
if(root==null)
return 0;
System.out.println("K Node:"+root.getData());
return 1;
}
return getNodeKNum(root.getLChild(),k-1)+getNodeKNum(root.getRChild(),k-1);
}
//查找某个节点
public Node findNode(Node root,int x){
if(root==null){
return null;
}
else if(root.getData()==x){
return root;
}
Node leftNode = findNode(root.getLChild(),x);
if(null!=leftNode)
return leftNode;
Node rightNode = findNode(root.getRChild(),x);
if(null!=rightNode)
return rightNode;
return null;
}
//返回某节点的父节点
public Node getParent(Node root, int x){
if(root==null)
return null;
Node childL = root.getLChild();
Node childR = root.getRChild();
if(childL!=null&&childL.getData()==x)
return root;
if(childR!=null&&childR.getData()==x)
return root;
Node parentL = getParent(root.getLChild(),x);
if(parentL!=null)
return parentL;
Node parentR = getParent(root.getRChild(),x);
if(parentR!=null)
return parentR;
return null;
}/** Queue说明
在java5中新增加了java.util.Queue接口,用以支持队列的常见操作。Queue接口与List、Set同一级别,都是继承了Collection接口。
Queue使用时要尽量避免Collection的add()和remove()方法,而是要使用offer()来加入元素,使用poll()来获取并移出元素。
它们的优点是通过返回值可以判断成功与否,add()和remove()方法在失败的时候会抛出异常。
如果要使用前端而不移出该元素,使用element()或者peek()方法
值得注意的是LinkedList类实现了Queue接口,因此我们可以把LinkedList当成Queue来用。
LinkedList实现了Queue接口。Queue接口窄化了对LinkedList的方法的访问权限(即在方法中的参数类型如果是Queue时,
就完全只能访问Queue接口所定义的方法 了,而不能直接访问 LinkedList的非Queue的方法),以使得只有恰当的方法才可以使用.
*/层次遍历:从根节点开始,每层从左至右,从上至下遍历每一个节点
实现方法,使用一个队列:
①取出一个节点,将他入队,
②若队列不为空,取出队列的头部元素并出队,若该元素左孩子不为空,左孩子入队;右孩子不为空,右孩子入队;
③重复②;
//层次遍历,用到队列
public void BTreeLevelOrder(){
Node root = this.root;
Queue <Node> queue = new LinkedList<Node>();
LinkedList<Node> list = new LinkedList<Node>();
queue.offer(root);
while(!queue.isEmpty()){
Node pre = queue.poll();
list.add(pre);
if(pre.getLChild()!=null)
queue.offer(pre.getLChild());
if(pre.getRChild()!=null)
queue.offer(pre.getRChild());
}
Iterator<Node> it = list.iterator();
while(it.hasNext()){
Node cur = (Node)it.next();
System.out.print(cur.getData()+", ");
}
}判断一棵树是否是完全二叉树,类似于层次遍历,使用队列;
层次遍历只入非空的队列,而判断完全二叉树,需要将空节点也入队;
当队头元素取出为空时,这时需要判断,剩下的队列里的所有元素是否都为空,
若都为空,则可判断它是完全二叉树,否则不是;
//判断一棵树是否是完全二叉树(层次遍历的变形)
public boolean isCompleteBTree(){
Node root = this.root;
Queue <Node> queue = new LinkedList<Node>();
queue.offer(root);
while(!queue.isEmpty()){
Node pre = queue.poll();
if(pre==null)
break;
queue.offer(pre.getLChild());
queue.offer(pre.getRChild());
}
while(!queue.isEmpty()){
Node cur = queue.poll();
if(cur!=null)
return false;
}
return true;
}
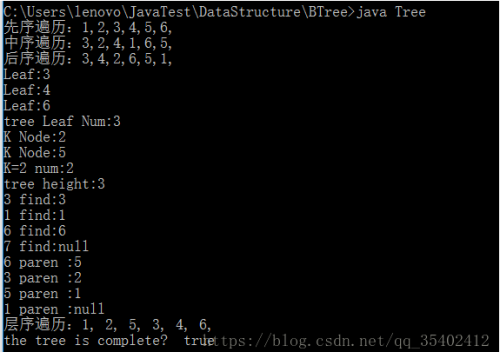
public static void main(String[] agrs){
Tree tree = new Tree();
int[] a = new int[]{1,2,3,'#','#',4,'#','#',5,6,'#','#','#' };
tree.root=tree.CreateBTree(a);
System.out.print("先序遍历:");
tree.prevOrder(tree.root);
System.out.print("\n中序遍历:");
tree.inOrder(tree.root);
System.out.print("\n后序遍历:");
tree.postOrder(tree.root);
System.out.println();
System.out.println("tree Leaf Num:"+tree.getLeaf(tree.root));
System.out.println("K=2 num:"+tree.getNodeKNum(tree.root,2));
System.out.println("tree height:"+tree.getHeight(tree.root));
System.out.println("3 find:"+tree.findNode(tree.root,3).getData());
System.out.println("1 find:"+tree.findNode(tree.root,1).getData());
System.out.println("6 find:"+tree.findNode(tree.root,6).getData());
System.out.println("7 find:"+tree.findNode(tree.root,7));
System.out.println("6 paren :"+tree.getParent(tree.root,6).getData());
System.out.println("3 paren :"+tree.getParent(tree.root,3).getData());
System.out.println("5 paren :"+tree.getParent(tree.root,5).getData());
System.out.println("1 paren :"+tree.getParent(tree.root,1));
System.out.print("层序遍历:");
tree.BTreeLevelOrder();
System.out.println();
System.out.println("the tree is complete? "+tree.isCompleteBTree());
}
}



小白过来学习